Hormones act like tiny messengers, traveling through the bloodstream to regulate mood, metabolism, growth, sleep, and reproduction. When even one of them drifts out of range, the effects can ripple through the entire body.
Hormonal imbalance is more common than many people realize, yet it often goes undiagnosed because its symptoms can be subtle, varied, or mistaken for everyday stress. This guide breaks down what’s really happening, why it matters, and how balance can be restored.
What Is Hormonal Imbalance?
Hormones are produced by glands such as the thyroid, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. A problem arises when the body makes too much or too little of one or more hormones, or when timing and feedback signals go wrong. Because hormones influence nearly every system, even small shifts can create noticeable physical or emotional changes over time.
Common Causes of Hormonal Imbalance
There isn’t a single trigger behind disrupted hormones. Often, several factors overlap. One major cause of hormonal imbalance is chronic stress, which keeps cortisol elevated and interferes with other hormones. Additional contributors include:
Poor sleep patterns and circadian rhythm disruption
Nutrient deficiencies, especially iodine, magnesium, and vitamin D
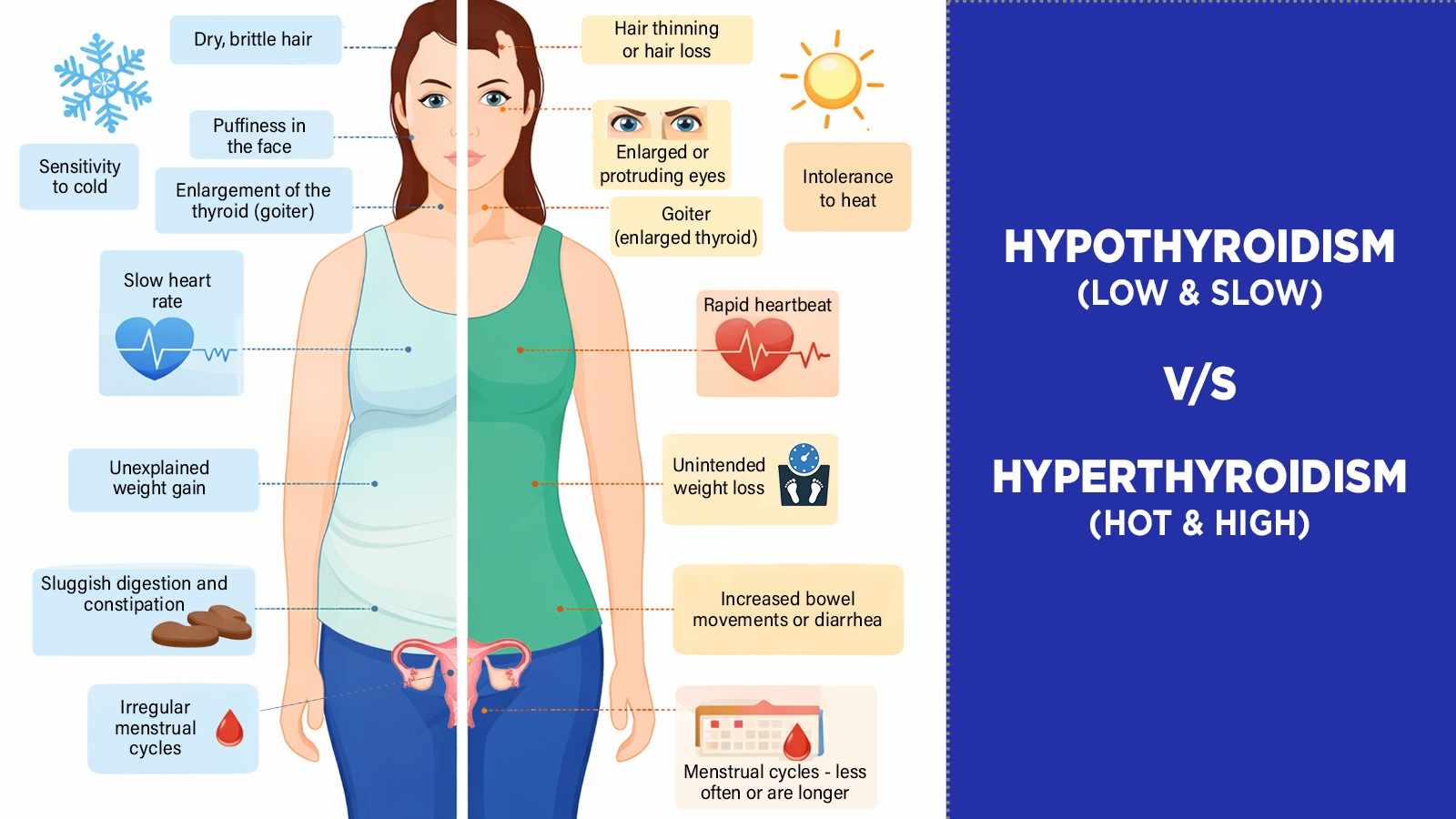
Medical conditions such as thyroid disorders, diabetes, or polycystic ovary syndrome
Certain medications, including steroids and hormonal contraceptives
Environmental toxins that mimic or block natural hormones
Lifestyle and health history usually determine how severe the disruption becomes.
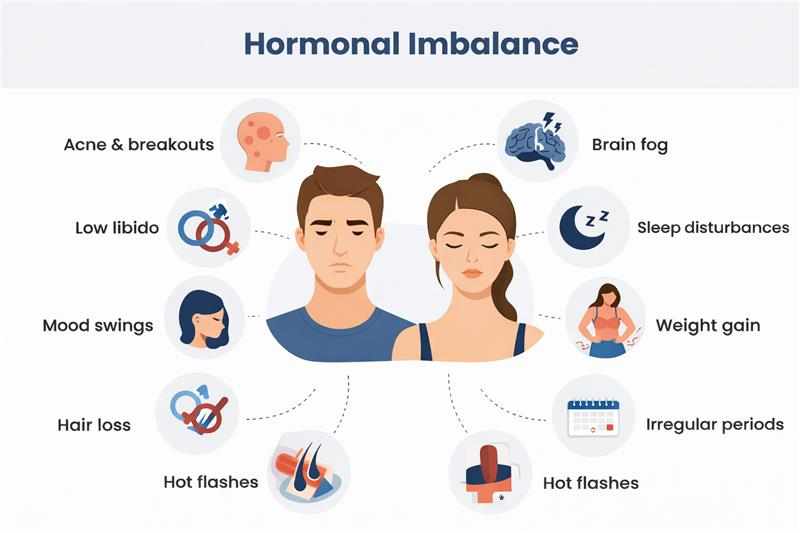
Hormonal Imbalance Symptoms in Women
In women, hormones fluctuate naturally across the lifespan, but persistent disruption can cause problems. Hormonal imbalance in females often shows up as:
Irregular, painful, or very heavy periods
Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight
Acne or skin changes beyond adolescence
Mood swings, anxiety, or depressive symptoms
Fertility challenges or low libido
These symptoms may worsen during puberty, after childbirth, or during perimenopause and menopause.
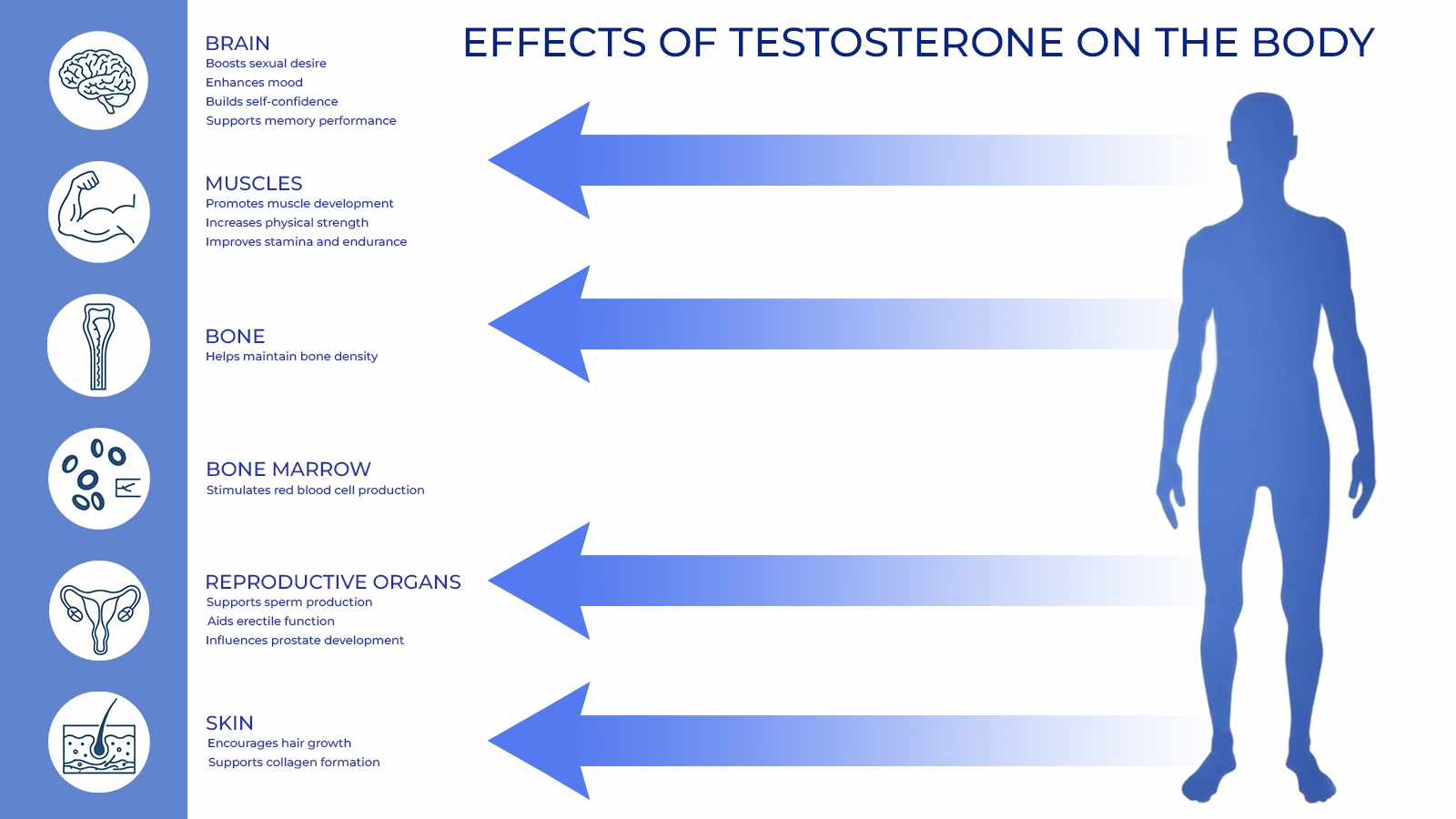
Hormonal Imbalance Symptoms in Men
Men also rely on finely tuned hormone levels for energy, muscle mass, and mental clarity. Hormonal imbalance in men may appear as:
Reduced sex drive or erectile difficulties
Loss of muscle and increased body fat
Fatigue and low motivation
Mood changes, including irritability or depression
Decreased bone density over time
Testosterone decline is often gradual, which is why these signs can be easy to miss at first.
General Symptoms Across All Genders
Some warning signs are not gender-specific and can affect anyone. These include:
Persistent tiredness despite adequate rest
Sleep disturbances or insomnia
Brain fog and poor concentration
Digestive issues such as bloating or constipation
Hair thinning or unusual hair growth patterns
Because these symptoms overlap with many conditions, hormones are not always the first thing considered.
Why Hormonal Imbalance Is Often Overlooked
Hormone-related symptoms tend to develop slowly. Many people normalize feeling “off” or attribute changes to aging, stress, or a busy lifestyle. Standard blood tests may also miss subtle fluctuations if they are taken at the wrong time or measure only a limited range of hormones. This combination leads to underdiagnosis and delayed care.
When to Seek Help for Hormone Issues
You should consider professional evaluation if symptoms persist for several months, worsen over time, or interfere with daily life. Sudden changes—such as rapid weight gain, missed periods, or severe mood shifts—also warrant attention. Early intervention can prevent complications and make treatment more effective.
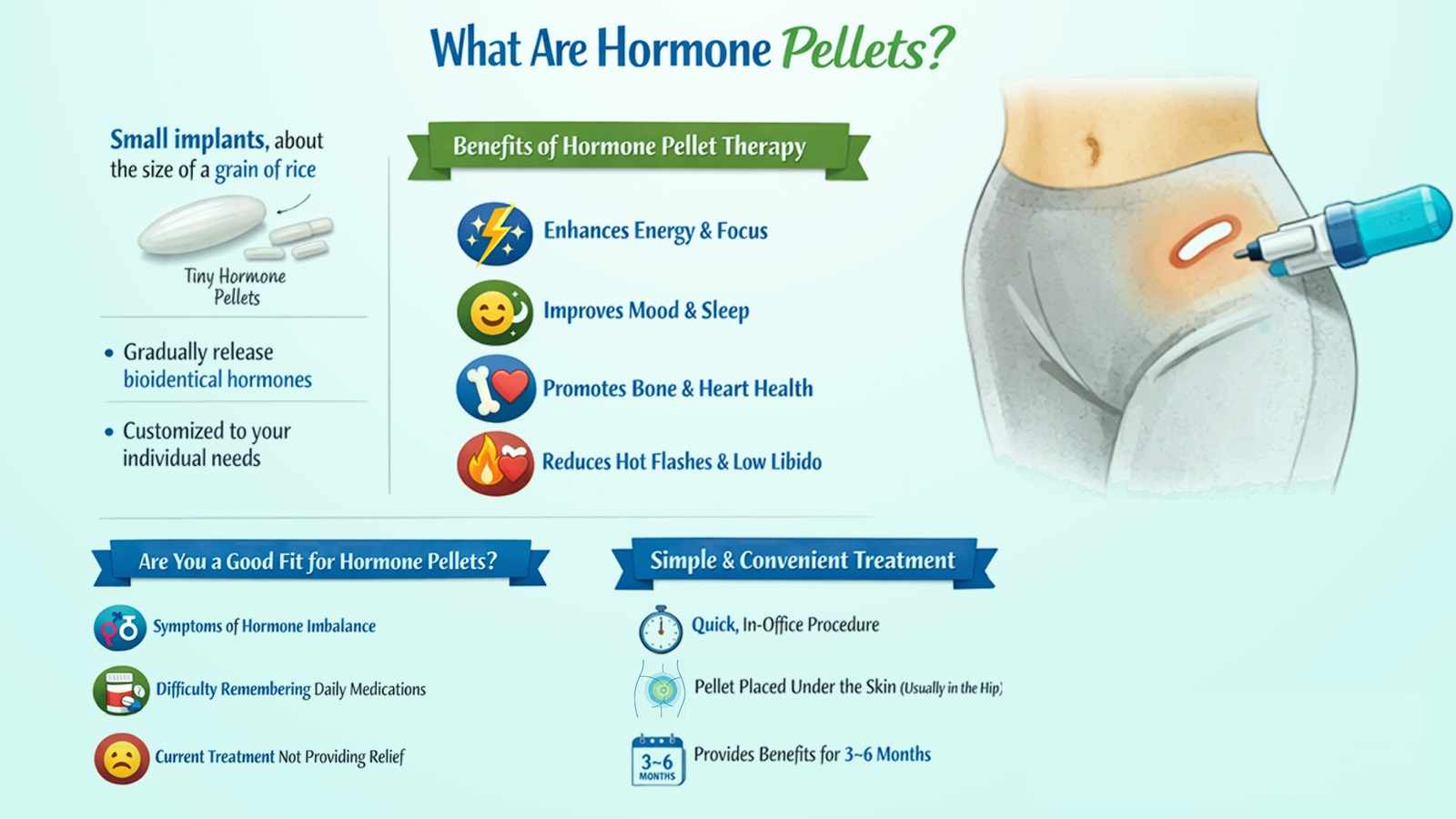
Learn more: What to Expect from Bioidentical Hormone Replacement Therapy (BHRT)
Hormone Testing and Diagnosis
Diagnosis usually starts with a detailed medical history and symptom review. Depending on the suspected issue, doctors may recommend:
Blood tests to measure hormone levels
Saliva or urine tests for daily hormone patterns
Imaging studies to check glands when needed
Accurate diagnosis often requires testing at specific times of day or points in the menstrual cycle.
Effective Hormonal Imbalance Treatments
Treatment depends on which hormones are affected and why. Options may include:
Hormone replacement or regulating medications
Treating underlying medical conditions
Targeted supplements under professional guidance
Dietary adjustments, including the best diet for hormonal imbalance, which emphasizes whole foods, healthy fats, adequate protein, and reduced refined sugar
Most treatment plans work best when medical care and lifestyle changes are combined.
Restoring Balance: Lifestyle and Next Steps
Long-term balance isn’t just about prescriptions. Daily habits play a huge role in hormone health. Prioritize consistent sleep, manage stress through relaxation or movement, and stay physically active without overtraining. Limiting alcohol, avoiding smoking, and reducing exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals can also support recovery. With patience and the right approach, many people see meaningful improvement.



Write a comment ...