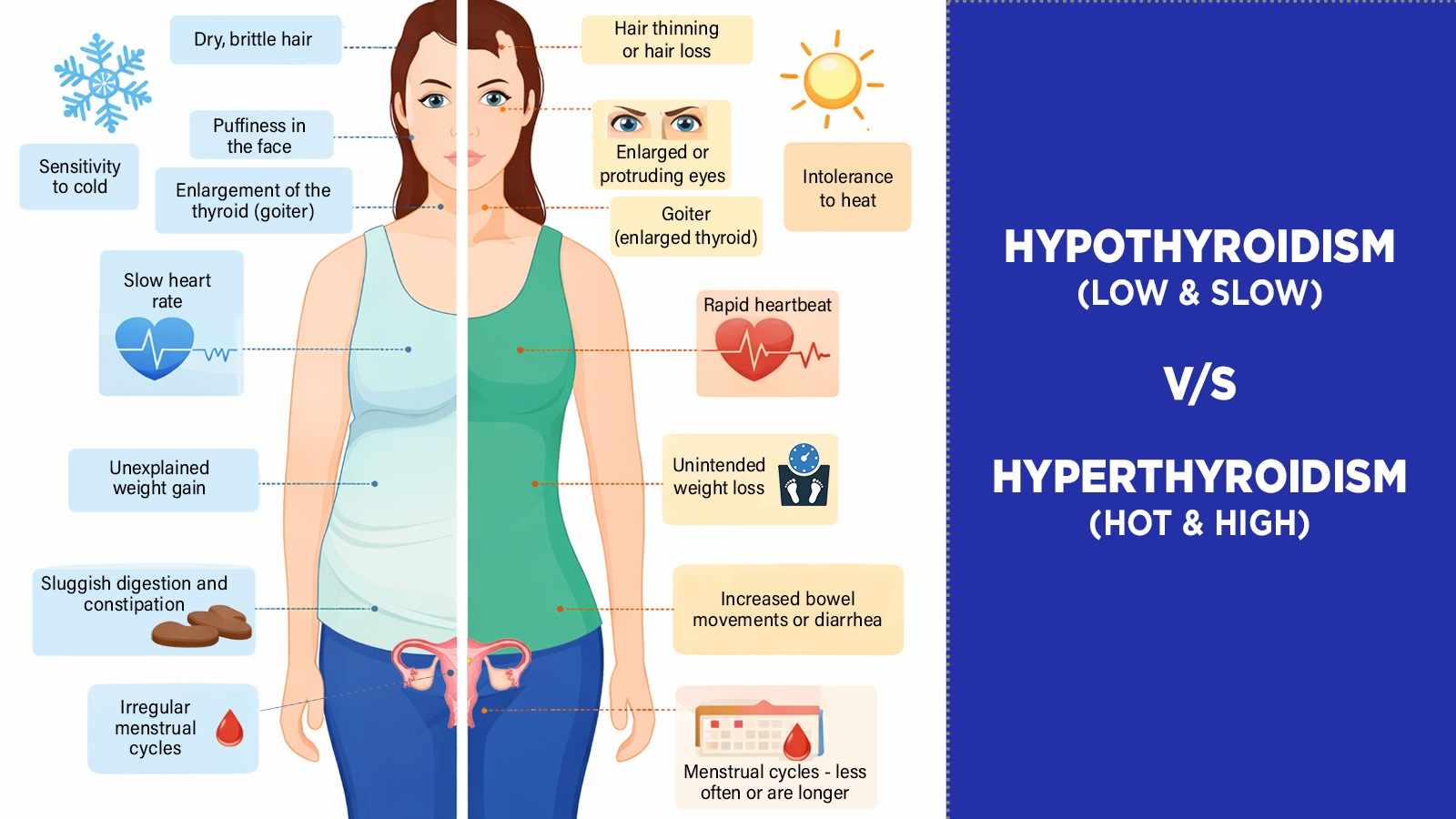
The thyroid gland may be small, but its influence on your body is enormous. Shaped like a butterfly and located at the base of your neck, this gland regulates metabolism, energy, heart rate, temperature, and even mood. When it produces too little or too much hormone, the entire system can fall out of balance.
What Is Hypothyroidism? – Underactive Thyroid Explained
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones, mainly T3 and T4. These hormones control how fast your body uses energy and how your organs function.
When levels are low, the body slows down. Metabolism decreases, cells work less efficiently, and many bodily systems begin to lag. Hypothyroidism often develops gradually, making it easy to overlook early signs.
This condition is more common in women and older adults, but it can affect people of any age, including children.
What Is Hyperthyroidism? – Overactive Thyroid Basics
Hyperthyroidism is the opposite problem: the thyroid produces too much hormone. This excess pushes the body into overdrive, accelerating metabolism and overstimulating organs.
People with hyperthyroidism often feel like their internal engine is running too fast. The condition can appear suddenly or develop over time, and it may fluctuate in severity.
One of the most common causes is Graves’ disease, an autoimmune condition that stimulates the thyroid to overproduce hormones.
Key Differences: Hypo vs Hyperthyroidism Comparison
Although both are thyroid disorders, their effects are quite different:
Hormone levels: Low in hypothyroidism, high in hyperthyroidism
Metabolism: Slowed vs accelerated
Heart rate: Slower or normal vs rapid or irregular
Weight changes: Weight gain vs unintended weight loss
Energy levels: Fatigue vs restlessness
Understanding these contrasts helps patients and clinicians tailor diagnosis and treatment more accurately.
Common Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism symptoms often develop subtly and worsen over time. Common signs include:
Persistent fatigue
Weight gain despite normal eating
Cold intolerance
Dry skin and hair
Constipation
Depression or low mood
Slow heart rate
Memory and concentration problems
Because these symptoms overlap with aging or stress, many people remain undiagnosed for years.
Common Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism usually produces more dramatic symptoms, such as:
Unexplained weight loss
Rapid or irregular heartbeat
Anxiety and irritability
Heat intolerance
Excessive sweating
Tremors in hands or fingers
Difficulty sleeping
Frequent bowel movements
Left untreated, hyperthyroidism can lead to serious heart and bone complications.
Main Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can trigger thyroid disorders:
For hypothyroidism:
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (autoimmune)
Thyroid surgery or radiation
Certain medications
Iodine deficiency (rare in developed countries)
For hyperthyroidism:
Graves’ disease
Thyroid nodules producing excess hormone
Inflammation of the thyroid (thyroiditis)
Excess iodine intake
Risk factors include family history, autoimmune disease, pregnancy, and being female.
How Thyroid Disorders Are Diagnosed
Diagnosis usually begins with a blood test measuring:
TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone)
Free T4 and sometimes T3
In hypothyroidism, TSH is high and T4 is low. In hyperthyroidism, TSH is low and T4 or T3 is high.
Additional tests may include:
Thyroid antibody tests
Ultrasound imaging
Radioactive iodine uptake scans
These help identify the underlying cause and guide treatment decisions.
Treatment Options for Hyperthyroidism
Treatment aims to reduce excess hormone production and control symptoms. Options include:
Antithyroid medications to block hormone production
Beta-blockers to control heart rate and tremors
Radioactive iodine therapy to shrink or destroy thyroid tissue
Surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid
The choice depends on age, cause, severity, and personal health factors.
Make an appointment for: Thyroid replacement therapy
Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy for Hypothyroidism
For hypothyroidism, treatment usually involves replacing the missing hormone with synthetic or natural preparations. This restores normal hormone levels and relieves symptoms.
Treatment typically includes:
Daily oral medication
Regular blood tests to adjust dosage
Long-term or lifelong therapy
Most patients feel significantly better within weeks, though fine-tuning the dose may take months.
Consistency is critical. Missing doses or changing brands without guidance can disrupt hormone balance and bring symptoms back.
Learn more: Top 10 Nutrients for Optimized Thyroid Health
Living with Thyroid Conditions: Monitoring and Tips
Managing a thyroid disorder is often a long-term commitment, but most people live full, healthy lives with proper care.
Helpful tips include:
Take medication at the same time daily
Avoid mixing thyroid medication with calcium or iron
Schedule regular blood tests
Track symptoms and report changes
Maintain a balanced diet and manage stress
Staying informed and engaged in your care makes a measurable difference in outcomes.
FAQs
1. Can thyroid disorders be cured permanently?
Some causes of hyperthyroidism can be cured with radioactive iodine or surgery. Hypothyroidism usually requires lifelong medication, but it is very manageable.
2. How often should thyroid levels be checked?
After diagnosis or medication changes, tests are often done every 6–8 weeks. Once stable, most people need testing once or twice a year.


Write a comment ...